Purisal Nebuliser Solution(Levosalbutamol)
Therapeutic Group: Respiratory
Presentation
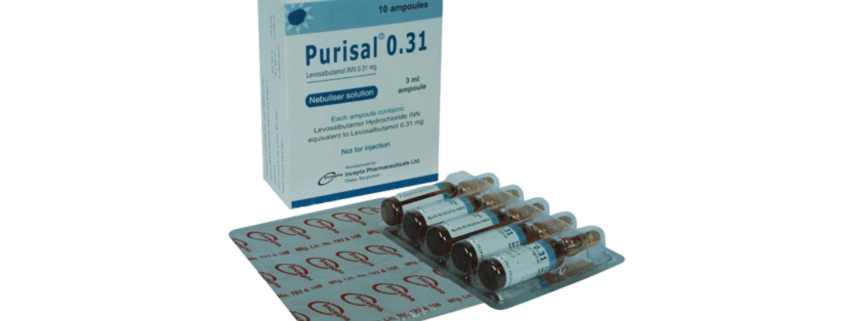
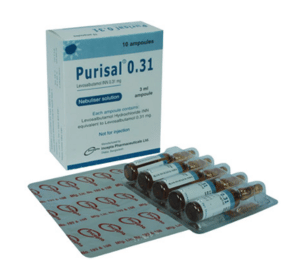
Purisal 0.31 mg: Each 3 ml ampoule contains Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride INN equivalent to Levosalbutamol 0.31 mg.
Purisal 0.63 mg: Each 3 ml ampoule contains Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride INN equivalent to Levosalbutamol 0.63 mg.
Purisal 1.25 mg: Each 3 ml ampoule contains Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride INN equivalent to Levosalbutamol 1.25 mg.
Description
Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution is a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution of the hydrochloride salt of Levosalbutamol, the (R)-enantiomer of the drug substance racemic salbutamol. Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride is a relatively selective beta – 2 – adrenergic receptor agonist. The molecular weight of Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride is 275.8, and its empirical formula is C13 H21 NO3 HCl.
Activation of beta – 2 – adrenergic receptors on airway smooth muscle leads to the activation of adenylcyclase and to an increase in the intracellular concentration of cyclic-3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). This increase in cAMP leads to the activation of protein kinase A, which inhibits the phosphorylation of myosin and lowers intracellular ionic calcium concentrations, resulting in relaxation. Levosalbutamol relaxes the smooth muscles of all airways, from the trachea to the terminal bronchioles. Levosalbutamol acts as a functional antagonist to relax the airway irrespective of the spasmogen involved, thus protecting against all bronchoconstrictor.
Indications
Purisal Nebuliser Solution is indicated for the treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in adults, adolescents, and children with reversible obstructive airway disease.
Dosage & Administration
Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution is supplied in unit-dose ampoules and requires no dilution before administration by nebulization.
Children (6 months-11 years): The recommended dosage is 0.31 mg administered three times a day, by nebulization. Routine dosing should not exceed 0.63 mg three times a day.
Adults and Adolescents above 12 years old: The recommended starting dosage is 0.63 mg administered three to four times a day, every 6 to 8 hours, by nebulization.
Patients 12 years of age and older with more severe asthma or patients who do not respond adequately to a dose of 0.63 mg of Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution may benefit from a dosage of 1.25 mg three times a day.
Side Effects
Potentially serious hypokalaemia may result from beta 2 – agonist therapy. This effect may be potentiated by hypoxia. Other side effects such as palpitation, fine tremors of the skeletal muscle (particularly the hand) and muscle cramps may occur. In few cases nervousness, headache, dizziness, fatigue and sleeplessness have also been reported.
Precautions
Levosalbutamol Hydrochloride, like all sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; in patients with convulsive disorders, hyperthyroidism, or diabetes mellitus; and in patients who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines.
Purisal Nebuliser Solution must not be injected.
Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution in pregnant women. Levosalbutamol Solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Lactation: It is not known whether Levosalbutamol is excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution is administered to a nursing woman.
Drug Interaction
Other short-acting sympathomimetic aerosol bronchodilators or epinephrine should be used with caution with Levosalbutamol. If additional adrenergic drugs are to be administered by any route, they should be used with caution to avoid deleterious cardiovascular effects.
Beta-blockers: Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists such as Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution, but may also produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients. However, under certain circumstances, e.g. prophylaxis after myocardial infarction, there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of beta-adrenergic blocking agents in patients with asthma. In this setting, cardio selective beta-blockers could be considered with caution.
Diuretics: The ECG changes and/or hypokalemia that may result from the administration of non-potassium sparing diuretics can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists when the recommended dose of the beta-agonist is exceeded.
Digoxin: It is necessary to carefully evaluate the serum digoxin levels in patients who are currently receiving digoxin and Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors or Tricyclic Antidepressants: Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents.
Over Dose
The expected symptoms with over dosage are those of excessive beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation and/or occurrence or exaggeration of any of the symptoms listed under side effects. Treatment consists of discontinuation of Levosalbutamol Nebuliser Solution together with appropriate symptomatic therapy. The judicious use of a cardioselective beta-receptor blocker may be considered.
Storage
Do not store above 30°C. Keep away from light and out of the reach of children.
Commercial Pack
Purisal 0.31 Nebuliser solution: Each box contains 10 ampoules in blister packs.
Purisal 0.63 Nebuliser solution: Each box contains 10 ampoules in blister packs.
Purisal 1.25 Nebuliser solution: Each box contains 10 ampoules in blister packs.