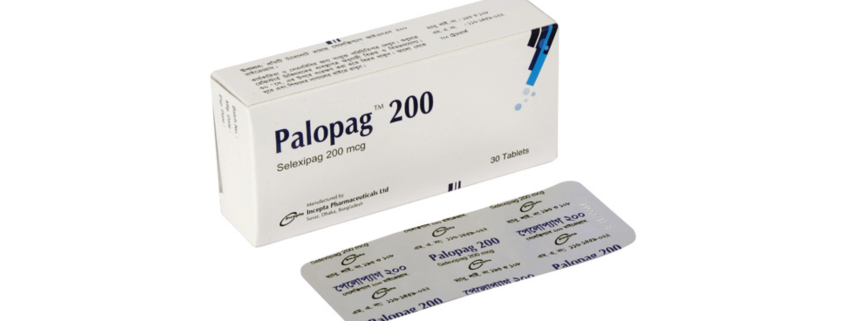
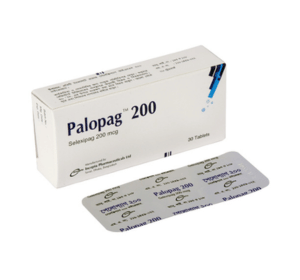
Palopag(Selexipag)
Therapeutic Group: Others
Presentation
Palopag 200: Each film coated tablet contains Selexipag INN 200 mcg.
Palopag 400: Each film coated tablet contains Selexipag INN 400 mcg.
Description
Selexipag is a selective non-prostanoid IP prostacyclin receptor agonist. Selexipag is a pale yellow crystalline powder that is practically insoluble in water. In the solid state selexipag is very stable, is not hygroscopic, and is not light sensitive. Selexipag is an oral prostacyclin receptor (IP receptor) agonist that is structurally distinct from prostacyclin. Selexipag is hydrolyzed by carboxylesterase 1 to yield its active metabolite, which is approximately 37-fold as potent as selexipag. Selexipag and the active metabolite are selective for the IP receptor versus other prostanoid receptors (EP1-4, DP, FP, and TP).
Indications
Selexipag is indicated for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH, WHO Group I) to delay disease progression and reduce the risk of hospitalization for PAH.
Dosage & Administration
The recommended starting dose is 200 mcg twice daily. Tolerability may be improved when taken with food. Increase the dose by 200 mcg twice daily at weekly intervals to the highest tolerated dose up to 1600 mcg twice daily. Maintenance dose is determined by tolerability.
Hepatic impairment: For Moderate hepatic impairment patients starting dose is 200 mcg once daily, increase the dose by 200 mcg once daily at weekly intervals to the highest tolerated dose up to 1600 mcg.
Avoid use of Selexipag in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C).
Side Effects
The most common side-effects of selexipag are Nausea, Diarrhoea, Vomiting, Headache, Jaw pain, muscle pain, low appetite and low RBC count.
Precautions
Discontinue Selexipag if the patient develops the sign and symptoms of Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease (PVOD).
Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnant women: There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with Selexipag in pregnant women
Nursing mother: It is not known if Selexipag is present in human milk. Selexipag or breast feeding should be discontinued in nursing mother.
Pediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric use: No overall differences have been observed.
Severe hepatic impairment: Avoid the use of Selexipag in severe hepatic impairment patients
Drug Interaction
• Moderate CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., deferasirox and teriflunomide) may increase exposure to the active metabolite of Selexipag
• CYP2C8 inducers (e.g., rifampicin) decrease exposure to the active metabolite & Increase concentration up to twice the dose of Selexipag
Over Dose
Isolated cases of overdose up to 3200 mcg were reported. Mild transient nausea was the only reported consequence. In the event of overdose, supportive measures must be taken as required.
Storage
Do not store above 30 C. Keep away from light and out of the reach of children.
Commercial Pack
Palopag 200: Each box contains 3 blister strips of 10 tablets.
Palopag 400: Each box contains 3 blister strips of 10 tablets.