Esipram(Escitalopram)
Therapeutic Group: Drugs of Nervous System
Presentation
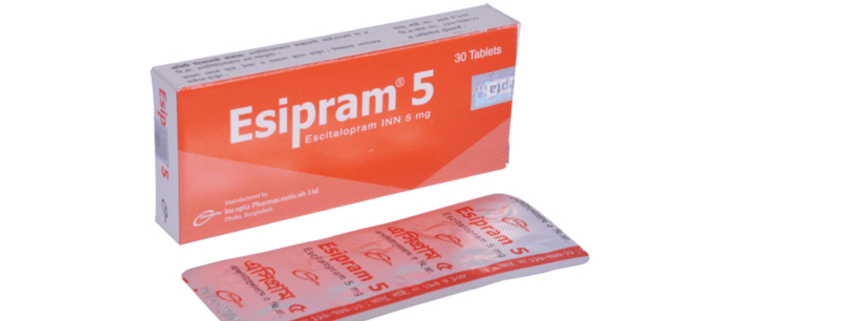
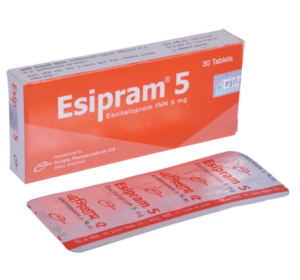
Esipram 5: Each tablet contains Escitalopram INN 5 mg (as Escitalopram Oxalate).
Esipram 10: Each tablet contains Escitalopram INN 10 mg (as Escitalopram Oxalate).
Description
The antidepressant action of escitalopram is presumably linked to the potentiation of serotonergic activity in the central nervous system (CNS) resulting from its inhibitory effect on the reuptake of 5-HT from the synaptic cleft. Escitalopram is the S-enantiomer of the racemate citalopram and is the enantiomer to which the therapeutic activity is attributed. Pharmacological studies have shown that the R-enantiomer is not inert but counteracts the serotonin-enhancing properties of the S-enantiomer in citalopram. Escitalopram has high affinity for the primary binding site and an allosteric modulating effect on the serotonin transporter.
Indications
• Depressive illness
• Generalized anxiety disorder
• Obsessive-compulsive disorder
• Social anxiety disorder
Dosage & Administration
Depressive illness, Generalized anxiety disorder & Obsessive-compulsive disorder : Adult over 18 years, 10 mg once daily increased if necessary to max. 20 mg daily; elderly initially half adult dose, lower maintenance dose may be sufficient; child not recommended: Panic disorder : Adult over 18 years, initially 5 mg once daily increased to 10 mg daily after 7 days; max. 20 mg daily; elderly initially half adult dose, lower maintenance dose may be sufficient; Social anxiety disorder : Adult over 18 years, initially 10 mg once daily adjusted after 2-4 weeks; usual dose 5-20 mg daily.
Side Effects
Escitalopram is well tolerated by most people. The most commonly reported side-effects of Escitalopram are nausea, insomnia, problems with ejaculation, drowsiness, increased sweating and fatigue. Most of the side-effects experienced by patients taking Escitalopram are mild and go away with continued treatment and usually do not cause patients to stop taking Escitalopram.
Precautions
Escitalopram should be used with caution in patients with epilepsy (avoid if poorly controlled, discontinue if convulsions develop), cardiac disease, diabetes mellitus, susceptibility to angle-closure glaucoma, a history of mania or bleeding disorders (especially gastro-intestinal bleeding) and if used with other drugs that increase the risk of bleeding, hepatic impairment, renal impairment, pregnancy and breast-feeding. It should also be used with caution in those receiving concurrent electroconvulsive therapy. Escitalopram may also impair performance of skilled tasks (e.g. driving).
Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
Category C. No relevant epidemiological data or well controlled studies in pregnant women are available for escitalopram. Escitalopram has had limited use in pregnancy without a reported increase in birth defects. Neonates should be observed if maternal use of Escitalopram continues into the later stages of pregnancy, particularly in the third trimester. Abrupt discontinuation should be avoided during pregnancy. This drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed and only after careful consideration of the risk/benefit. It is expected that escitalopram, like citalopram, will be excreted into human breast milk.
Drug Interaction
Escitalopram should not be started until 2 weeks after stopping an MAOI. Conversely, an MAOI should not be started until at least a week after escitalopram or related antidepressant has been stopped.
Commercial Pack
Esipram 5: Each box contains 3 blister strips of 10 tablets. Esipram 10: Each box contains 3 blister strips of 10 tablets.