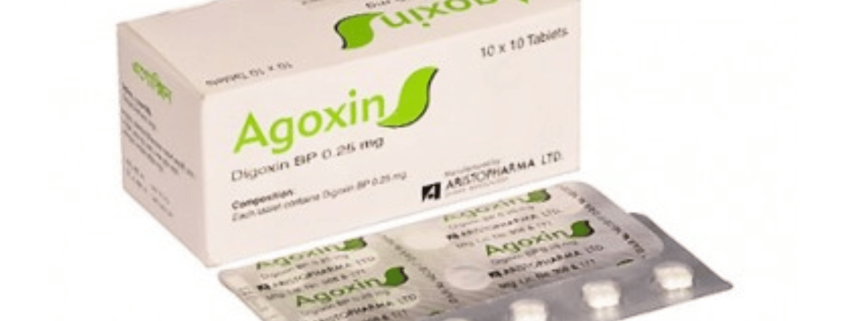
Agoxin
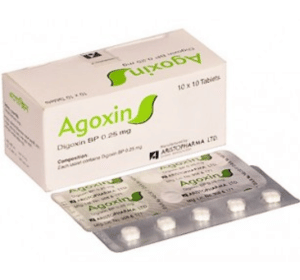
Digoxin
Indications
1. Heart failure
2. Atrial fibrillation with an uncontrolled ventricular rate
3. Acute left ventricular failure
4. Chronic left ventricular failure and congestive heart failure, especially when caused by hypertensive valvular (especially mitral valvular) disease or ischaemic heart disease.
Dosage & Administration
For rapid action 1-1.5 mg in divided doses over 24 hours for less urgent digitalisation 0.25-0.5 mg daily(higher dose may be divided); Maintenance: 0.0625 – 0.5 mg daily (higher dose may be divided) accordingly to renal function and in atrial fibrilation on heart rate response; usual range: 0.125-0.25 mg daily (lower dose my be appropriate in elderly).
Side effects
Usually associated with excessive dosage include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, visual disturbance, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, confusion, delirium, hallucination, depression, arrhythmia, heart block, intestinal ischaemia, gynaecomastia on long term use, thrombocytopenia reported.
Description
Digoxin is a cardiac glycoside used in the management of particularly atrial fibrillation and in heart failure. The principal actions of digoxin are an increase in the force of myocardial contraction (positive inotropic activity) and a reduction in the conductivity of the heart particularly in conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) +node. Digoxin also has a direct action on vascular smooth muscle and indirect effects mediated primarily by the autonomic nervous system and particularly by an increase in the vagal activity.