Abetis Tablet
Olmesartan Medoxomil
Indications
Abetis is indicated for the treatment of hypertension. It may be used alone or in combination with other antihypertensive agents.
Pharmacology
Angiotensin II is formed from angiotensin I in a reaction catalyzed by angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE, Kininase II). Angiotensin II is the principal pressor agent of the renin-angiotensin system, with effects that include vasoconstriction, stimulation of synthesis and release of aldosterone, cardiac stimulation and renal reabsorption of sodium. Olmesartan blocks the vasoconstrictor effects of angiotensin II by selectively blocking the binding of angiotensin II to the AT 1 receptor in vascular smooth muscle. An AT 2 receptor is found also in many tissues, but this receptor is not known to be associated with cardiovascular homeostasis. Olmesartan has more than a 12,500-fold greater affinity for the AT 1 receptor than for the AT 2 receptor. Olmesartan medoxomil does not inhibit ACE (kininase II), it does not affect the response to bradykinin. Blockade of the angiotensin II receptor inhibits the negative regulatory feedback of angiotensin II on renin secretion, but the resulting increased plasma renin activity and circulating angiotensin II levels do not overcome the effect of olmesartan on blood pressure.
Dosage & Administration
Dosage must be individualized. The usual recommended starting dose of Olmesartan is 20 mg once daily when used as monotherapy in patients who are not volume-contracted. For patients requiring further reduction in blood pressure after 2 weeks of therapy, the dose of Olmesartan may be increased to 40 mg. Doses above 40 mg do not appear to have a greater effect. Twice-daily dosing offers no advantage over the same total dose given once daily.
No initial dosage adjustment is recommended for elderly patients, for patients with moderate to marked renal impairment (creatinine clearance <40 ml/min) or with moderate to marked hepatic dysfunction. For patients with possible depletion of intravascular volume (e.g. patients treated with diuretics, particularly those with impaired renal function), Olmesartan should be initiated under close medical supervision and consideration should be given to use of a lower starting dose. Olmesartan may be administered with or without food.
Paediatric use: Safety and effectiveness in paediatric patients have not been established.
Interaction
No significant drug interactions were reported in studies in which Abetis was co-administered with digoxin or warfarin in healthy volunteers. The bioavailability of olmesartan was not significantly altered by the co-administration of antacids. Abetis is not metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system and has no effects on P450 enzymes; thus, interactions with drugs that inhibit, induce, or are metabolized by those enzymes are not expected. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) including selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors (COX-2 Inhibitors) in patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or with compromised renal function, co-administration of NSAIDs, including selective COX-2 inhibitors, with angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including Abetis, may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible. Monitor renal function periodically in patients receiving Abetis and NSAID therapy. The antihypertensive effect of angiotensin II receptor antagonists, including Abetis may be attenuated by NSAIDs including selective COX-2 inhibitors.
Contraindications
Olmesartan is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product.
Side Effects
Abetis has been evaluated for safety in more than 3825 patients/subjects, including more than 3275 patients treated for hypertension in controlled trials. Treatment with Abetis was well tolerated, with an incidence of adverse reactions similar to placebo. The overall frequency of adverse reactions was not dose related. Analysis of gender, age and race groups demonstrated no differences between Abetis and placebo treated patients. The rate of withdrawals due to adverse reactions in all trials of hypertensive patients was 2.4% of patients treated with Abetis and 2.7% of control patients. In placebo controlled trials, the only adverse reaction that occurred in more than 1% of patients treated with Abetis and at a higher incidence versus placebo was dizziness (3% vs. 1%)
The following adverse reactions occurred in placebo-controlled clinical trials at an incidence of more than 1% of patients treated with Abetis, but also occurred at about the same or greater incidence in patients receiving placebo: back pain, bronchitis, creatine phosphokinase increased, diarrhea, headache, hematuria, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, influenza-like symptoms, pharyngitis, rhinitis and sinusitis. The incidence of cough was similar in placebo (0.7%) and Abetis (0.9%) patients.
Pregnancy & Lactation
When pregnancy is detected, discontinue this product as soon as possible. When used in pregnancy during the second and third trimesters, drugs that act directly on the renin-angiotensin system can cause injury and even death to the developing fetus. It is not known whether Olmesartan is excreted in human milk, but Olmesartan is secreted at low concentration in the milk of lactating rats. Because of the potential for adverse effects on the nursing infant, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Precautions & Warnings
As a consequence of inhibiting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, changes in renal function may be anticipated in susceptible individuals treated with Abetis. In patients whose renal function may depend upon the activity of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (e.g. patients with severe congestive heart failure), treatment with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor antagonists has been associated with oliguria and/or progressive azotemia and (rarely) with acute renal failure and/or death. Similar results may be anticipated in patients treated with Abetis.
Overdose Effects
There is no experience of overdose with Abetis. The most likely effects of Abetis overdosage are hypotension and tachycardia; bradycardia could be encountered if parasympathetic (vagal) stimulation occurred. If intake is recent, gastric lavage or induction of emesis may be considered. Clinically significant hypotension due to an overdose of Abetis requires the active support of the cardiovascular system, including close monitoring of heart and lung function, the elevation of the extremities, and attention to circulating fluid volume and urine output.
Therapeutic Class
Angiotensin-ll receptor blocker
Storage Conditions
Store in cool & dry place below 30ºC, protect from light & moisture. Keep out of the reach of children.
Chemical Structure
| Molecular Formula : | C29H30N6O6 |
| Chemical Structure : | 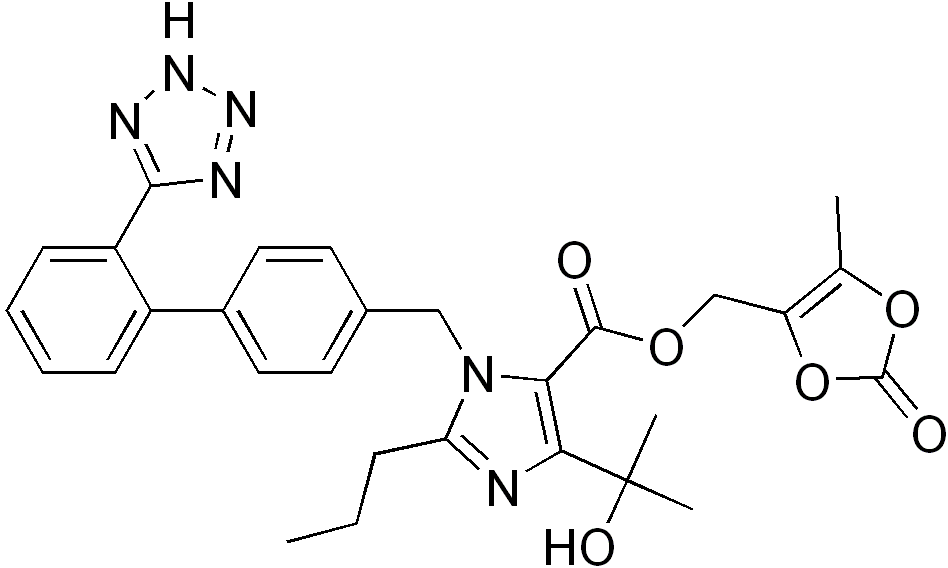 |
Common Questions about Abetis 20 mg Tablet
What are the uses of Abetis 20 mg Tablet?
Abetis 20 mg Tablet is Angiotensin II receptor blocker which is used to treat high blood pressure.
How long do I need to use Abetis 20 mg Tablet before I see improvement in my condition?
In most of the cases, the average time taken by Abetis 20 mg Tablet to reach its peak effect is around 1 day to 1 week. Please consult your doctor for the time period you need to use this medication.
At what frequency do I need to use Abetis 20 mg Tablet?
Abetis 20 mg Tablet is generally used once or twice a day. It is advised to consult your doctor before the usage, as the frequency also depends on the patient’s condition.
Should I use Abetis 20 mg Tablet empty stomach, before food or after food?
Abetis 20 mg Tablet is advised to be consumed orally. If you take it on an empty stomach, it might upset the stomach. Please consult the doctor before using it.
What are the instructions for the storage and disposal of Abetis 20 mg Tablet?
It should be stored at room temperature, away from heat and direct light. Keep it away from the reach of children.
Quick Tips
- Take Abetis 20 mg Tablet at the same time every day to help you remember to take it.
- Abetis 20 mg Tablet can make you feel dizzy for the first few days. Rise slowly if you have been sitting or lying down for a long time.
- Your doctor may get regular tests done to monitor the level of urea, creatinine, and potassium in your blood.
- Avoid taking anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen along with this medicine without consulting your doctor.
- Abetis 20 mg Tablet may increase the level of potassium in the blood. Avoid taking potassium supplements and potassium-rich foods such as banana fruit juice, coconut water, and broccoli.
- Do not take Abetis 20 mg Tablet if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Do not stop taking it suddenly without talking to your doctor.