Proton-P (Pantoprazole)
Therapeutic Group : Antiulcerant
Presentation:
Proton-P Tablet 20 mg : Each enteric coated tablet contains Pantoprazole Sodium Sesquihydrate USP equivalent to Pantoprazole 20 mg.
Proton-P Tablet 40 mg : Each enteric coated tablet contains Pantoprazole Sodium Sesquihydrate USP equivalent to Pantoprazole 40 mg.
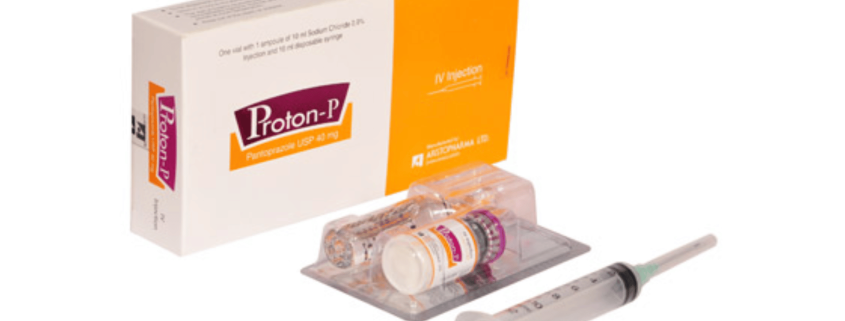
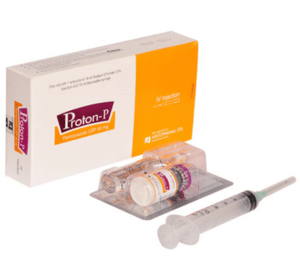
Proton-P IV Injection: Each vial contains lyophilized Pantoprazole Sodium Sesquihydrate USP equivalent to Pantoprazole 40 mg.
Indications:
Proton-P Tablet : Proton-P is indicated for the following purposes:
Duodenal ulcer, benign gastric ulcer, esophagitis/ulceration. Zollinger-Ellision syndrome. resistant ulcers, eradication of Helicobacter pylori in the treatment of peptic ulcer (in combination with antibiotics) and in the treatment of ulcers induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Proton-P IV Injection : Proton-P IV injection is indicated where oral therapy is not appropriate such as duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, reflux esophagitis, gastrointestinal lesions refractory to H2 blockers, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome & maintenance of healed reflux esophagitis.
Dosage & Administration:
Proton-P Tablet : The usual starting dose is 40 mg once daily & maintenance dose is 20 mg once daily to be taken 30 minutes before breakfast. Duodenal ulcer : 40 mg daily in the morning for two weeks, continued for further two weeks if not fully healed. Gastric ulcer : 40 mg dally in the morning for four weeks, continued for further four weeks if not fully healed. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease : 40 mg daily in the morning for four weeks, continued for further four weeks if not fully healed; may be continued at 20 mg daily (long-term management), increased to 40 mg daily if symptoms return. Duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori : 40 mg twice daily associated with appropriate antibiotic regimen. Ulcer induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Pantoprazole 40 mg daily in the morning has been used to prevent the formation of gastroduodenal lesions in patients receiving continuous treatment with NSAIDs. Gastro-intestinal bleeding from stress or acid peptic diseases : The usual adult oral dose is 40 mg once daily, preferably in the morning with or without food, if required dose may be increased.
Proton-P IV Injection :
| Indication | Dose |
|---|---|
| Duodenal ulcer, gastric ulcer, gastrointestinal lesions refractory to H2 blockers & Zollinger-Ellison syndrome | 40 mg daily |
| Reflux esophagitis | 20-40 mg daily |
Method of administration :
Injection :
Pantoprazole IV injection is obtained by adding 10 ml Sodium Chloride 0.9% injection to the vial containing powder. After reconstitution the injection should be given slowly over a period of at least 2 minutes. The injection should be used within 6 hours of reconstitution when stored at room temperature. Besides the resulting injection should be used within 12 hours when stored at 2-8°C.
Infusion :
Pantoprazole IV infusion should be reconstituted with 10 ml of Sodium Chloride 0.9% injection, and further diluted (admixed) with 100 ml Sodium Chloride 0.9% injection or 5% dextrose injection. The reconstituted injection may be stored for up to 24 hours at room temperature after reconstitution. The reconstituted infusion should be administered intravenously over a period of 15 minutes.
Contrainidications:
In patients with known hypersensitivity to Pantoprazole Sodium Sesquihydrate or any excipient of the formulation.
Warning & Precautions:
Proton pump inhibitors should be used with caution in patients with liver disease, in pregnancy and breast feeding, before treatment the presence of gastric malignancy should be excluded. No problem with Pantoprazole has been encountered in clinical use in elderly patients. No dosage adjustment of Pantoprazole is required in patients with renal impairment but prolongation of metabolism leading to a slight rise in peak plasma levels occurs in hepatic cirrhosis and it is recommended that the dosing is reduced to every other day.
Side effects:
Side effects of the proton pump inhibitors include gastro-intestinal disturbances (including diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting, constipation, flatulence, abdominal pain), headache hypersensitivity reactions (including rash, urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm), pruritus, dizziness, peripheral edema, muscle and joint pain, malaise, blurred vision, depression and dry mouth.
Drug interaction:
Pantoprazole does not react with the cytochrome P-450 system. No drug interaction has been reported in a large series of studies examining reactions with contraceptives, diazepam. diclofenac, ethanol, caffeine, metoprolol, theophylline, digoxin, phenytoin, nifedipine and warfarin.
Use in pregnancy: This drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Use in lactation: Pantoprazole is likely to be excreted in human milk, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Use in children : There are no data currently available on the use of Pantoprazole in children.
Packing:
Proton-P Tablet 20 mg : Box containing 60\\\\\\\’s tablets in alu-alu blister pack.
Proton-P Tablet 40 mg : Box containing 60\\\\\\\’s tablets in alu-alu blister pack.
Proton-P IV Injection : Each Box containing one vial of lyophilized Pantoprazole Sodium sesquihydrate powder with 1 ampoule of 10 ml Sodium Chloride 0.9% injection,10 ml disposable syringe, bandage alcohol pad.