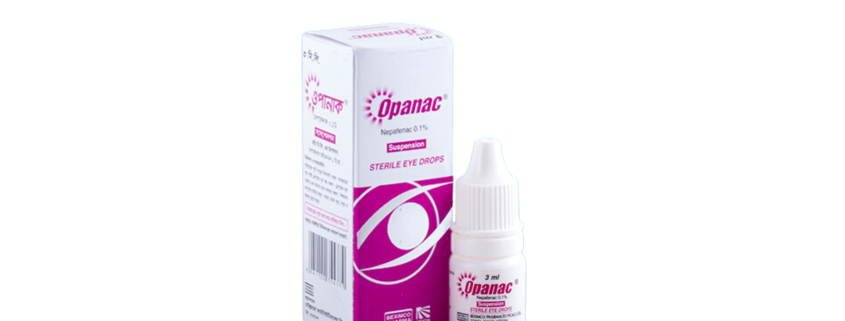
Opanac Eye drops
Generic Name: Nepafenac 0.1% ophthalmic suspension
Dosage Form: Drops
TG Name: Eye Care
1. What Opanac is and what it is used for?
Opanac eye drop contains Nepafenac which is a Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) prodrug for ophthalmic use.
2. Before you take Opanac
Do not take this medicine and tell your doctor if:
Nepafenac is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in the formula or to other NSAIDs.
Take special care with Tearo
Check with your doctor before taking this medicine if:
Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including Nepafenac, may slow or delay healing. Topical corticosteroids are also known to slow or delay healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical steroids may increase the potential for healing problems. Use of topical NSAIDs may result in keratitis. In some susceptible patients, continued use of topical NSAIDs may result in epithelial breakdown, corneal thinning, corneal erosion, corneal ulceration or corneal perforation. These events may be sight threatening. Patients with evidence of corneal epithelial breakdown should immediately discontinue use of topical NSAIDs including Nepafenac and should be closely monitored for corneal health.
Taking other medicines
No information available.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Nepafenac should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Nursing Mothers: It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Nepafenac ophthalmic suspension is administered to a nursing woman. Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Nepafenac in pediatric patients below the age of 10 years have not been established.
3. How to take Opanac?
Taking this medicine
Always use Opanac exactly as your doctor has told you. You should check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
How much to take
One drop of Nepafenac should be applied to the affected eye(s) three-times-daily beginning 1 day prior to cataract surgery, continued on the day of surgery and through the first 2 weeks of the postoperative period.
If you take more Opanac than you should
If you have too much of this medicine, talk to your doctor straight away.
If you stop taking Opanac (Do not need to change)
Do not stop taking this medicine without talking to your doctor. You should not stop taking Opanac just because you feel better. This is because the problem may come back or get worse again.
If you have any further questions on the use of this product, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Opanac can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The most frequently reported ocular adverse reactions following cataract surgery were capsular opacity, decreased visual acuity, foreign body sensation, increased intraocular pressure and sticky sensation. These reactions occurred in approximately 5 to 10% of patients. Other ocular adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of approximately 1 to 5% included conjunctival edema, corneal edema, dry eye, lid margin crusting, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia, ocular pain, ocular pruritus, photophobia, tearing and vitreous detachment. Some of these reactions may be the consequence of the cataract surgical procedure. Non-ocular adverse reactions reported at an incidence of 1 to 4% included headache, hypertension, nausea/vomiting and sinusitis.
Tell your doctor if any of the side effects gets serious or lasts longer than a few days, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet.
5. How to store Opanac?
Store in a cool and dry place, away from light. Keep out of reach of children. Shake well before each use.