Maxsulin(Human insulin rDNA)
Therapeutic Group: Bio Tech
Presentation
Maxsulin 30/70 injection 40 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin 30/70 injection 100 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin 50/50 injection 100 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 50% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 50% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin N injection 40 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as Isophane Insulin (NPH).
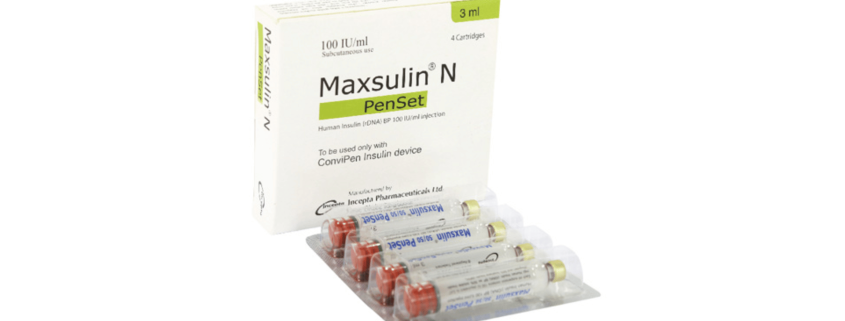
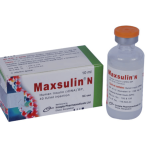
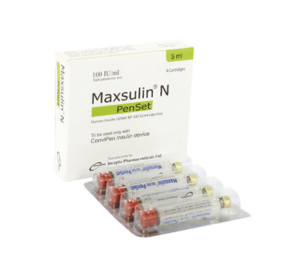
Maxsulin N injection 100 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin R injection 40 IU: Each ml solution contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).
Maxsulin R injection 100 IU: Each ml solution contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).
Maxsulin 30/70 PenSet injection 100 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin 50/50 PenSet injection 100 IU: Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 50% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 50% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin R PenSet injection 100 IU: Each ml solution contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).
Description
The blood glucose lowering effect of Insulin is due to the facilitated uptake of glucose following binding of Insulin to receptors on muscle and fat cells and to the simultaneous inhibition of glucose output from the liver.
Indications
Treatment of diabetes mellitus. Furthermore indicated for the initial stabilisation of diabetes, during treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperosmolar non ketotic syndrome, and during stress situations such as severe infections and major surgery in diabetic patients.
Instructions to be given to the patient
Vial
Before injecting this Insulin:
1. Disinfect the rubber stopper.
2. If suspension, roll the vial between the palms of the hands until the liquid is uniformly white and cloudy.
3. Draw into the syringe the same amount of air as the dose of insulin to be injected.
4. Inject the air into the vial.
5. Turn the vial and syringe upside down and draw the correct insulin dose into the syringe. Withdraw the needle from vial and expel the air from the syringe and check that the dose is correct.
6. Inject immediately.
Cartridge
Before injecting this Insulin:
1. According to the instruction given with ConviPen, insert the Maxsulin cartridge into the pen correctly & equip the needle
2. In case of Maxsulin 30/70 and Maxsulin 50/50, gently turn the pen upside down for 8-10 times until the insulin in the cartridge becomes uniformly mixed suspension
3. Remove the needle cap, discharge air bubbles in the catridge
4. Adjust the dosage button to get correct dose & inject to the specific site
5. In order to avoid cross contamination, do not let the needle touch anything during the process of preparation.
For detail description, please see the Patient Instruction Leaflet provided with ConviPen.
Dosage & Administration
Dosage is individualized and determined by the physician in accordance with the needs of the patient.
The average range of total daily Insulin requirement for maintenance therapy in type 1 diabetic patients lies between 0.5 and 1.0 IU/kg. However, in pre-pubertal children it usually varies from 0.7 to 1.0 IU/kg, but can be much lower during the period of partial remission. In Insulin resistance, e.g. during puberty or due to obesity, the daily Insulin requirement may be substantially higher.
Initial dosages for type 2 diabetic patients are often lower, e.g. 0.3 to 0.6 IU/kg/day.
An injection should be followed by a meal or snack containing carbohydrates within 30 minutes.
The preparations are administered subcutaneously in the thigh or abdominal wall. A subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall results in a faster absorption than from other injection sites.
Insulin suspensions are never to be administered intravenously.
Side Effects
Hypoglycaemia, severe hypoglycaemia may lead to unconsciousness and/or convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain function or even death.
Symptoms of generalised hypersensitivity may include generalised skin rash, itching, sweating, gastrointestinal upset, angioneurotic oedema, difficulties in breathing, palpitation and reduction in blood pressure.
Fast improvement in blood glucose control may be associated with a condition termed acute painful neuropathy, which is usually reversible. Lipodystrophy may occur at the injection site as a consequence of failure to rotate injection sites within an area. Injection site reactions (redness, swelling, itching, pain and haematoma at the injection site) may occur during treatment with Insulin. Most reactions are transitory and disappear during continued treatment. Oedema may occur upon initiation of Insulin therapy. These symptoms are usually of transitory nature.
Precautions
Inadequate dosing or discontinuation of treatment, especially in type 1 diabetes, may lead to hyperglycaemia. In type 1 diabetes, untreated hyperglycaemic events eventually leads to diabetic ketoacidosis which is potentially lethal.
Hypoglycaemia may occur if the Insulin dose is too high in relation to the Insulin requirement. If an adjustment is needed, it may occur with the first dose or during the first several weeks or months.
Patients whose blood glucose control is greatly improved, e.g. by intensified Insulin therapy, may experience a change in their usual warning symptoms of hypoglycaemia and should be advised accordingly.
Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
There are no restrictions on the treatment of diabetes with Insulin during pregnancy as Insulin does not pass the placental barrier.
There are no restrictions on the treatment of diabetes with Insulin during lactation, as Insulin treatment of the nursing mother involves no risk to the baby. However, the Insulin dosage, diet or both may need to be reduced.
Drug Interaction
A number of drugs are known to interact with the glucose metabolism. Possible interactions must therefore be taken into account by the physician.
The following substances may reduce the Insulin requirements:
Oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHA), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), non-selective beta-blocking agents, angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, salicylates and alcohol.
The following substances may increase the Insulin requirements:
Thiazides, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, beta-sympathomimetics, growth hormone and danazol.
Beta-blocking agents may mask the symptoms of hypoglycaemia and delay recovery from hypoglycaemia. Octreotide/lanreotide may both increase and decrease Insulin requirement. Alcohol may intensify and prolong the hypoglycaemic effect of Insulin.
Over Dose
Insulins have no specific overdose definitions. However, hypoglycaemia may develop over sequential stages:
Mild hypoglycaemic episodes can be treated by oral administration of glucose or sugary products. It is therefore recommended that the diabetic patient constantly carries some sugarlumps, sweets, biscuits or sugary fruit juice.
Severe hypoglycaemic episodes, where the patient has become unconscious, can be treated by glucagon (0.5 to 1 mg) given intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Glucose must also be given intravenously, if the patient does not respond to glucagon within 10 to 15 minutes.
Upon regaining consciousness, administration of oral carbohydrate is recommended for the patient in order to prevent relapse.
Storage
Store at 2°C to 8°C in a refrigerator. Do not freeze. Protect from light.
Commercial Pack
Maxsulin 30/70 injection 40 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin 30/70 injection 100 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin 50/50 jnjection 100 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 50% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 50% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin N jnjection 40 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin N injection 100 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin R injection 40 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml solution contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 40 IU (equivalent to 1.388 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).
Maxsulin R injection 100 IU: Each box contains 10 ml glass vial. Each ml solution contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).
Maxsulin 30/70 PenSet injection 100 IU: Each box contains 4 x 3 ml glass cartridges. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 30% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 70% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
The latest louboutin stiefeletten schwarz store offers high quality christian louboutin.
Maxsulin 50/50 PenSet injection 100 IU: Each box contains 4 x 3 ml glass cartridges. Each ml suspension contains Human Insulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as 50% soluble Insulin (Regular) and 50% Isophane Insulin (NPH).
Maxsulin R PenSet injection 100 IU: Each box contains 4 x 3 ml glass cartridges. Each ml solution contains Human I nsulin (rDNA) BP 100 IU (equivalent to 3.47 mg) as soluble Insulin (Regular).