Parinox(Enoxaparin Sodium)
Therapeutic Group: Cardiovascular
Presentation
Active ingredient: Enoxaparin Sodium BP.
Solvent: Water for injections BP.
Each ml of the solution contains: 10000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to 100 mg Enoxaparin Sodium.
Parinox 20: Each pre-filled syringe (0.2ml) contains 2000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to Enoxaparin Sodium BP 20 mg.
Parinox 40: Each pre-filled syringe (0.4ml) contains 4000 anti-Xa IU is equivalent to 40 mg Enoxaparin Sodium BP.
Parinox 60: Each pre-filled syringe (0.6ml) contains 6000 anti-Xa IU is equivalent to 60 mg Enoxaparin Sodium BP.
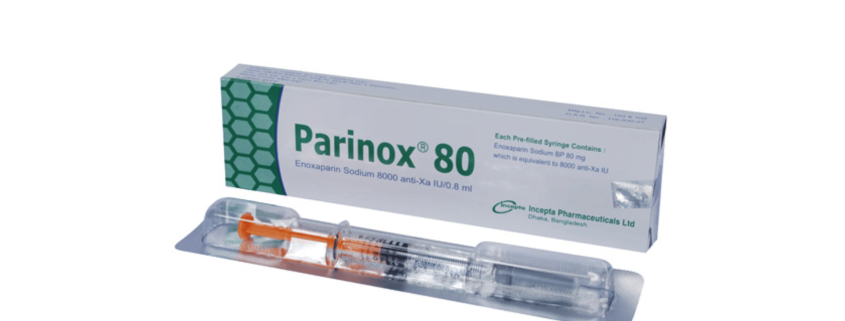
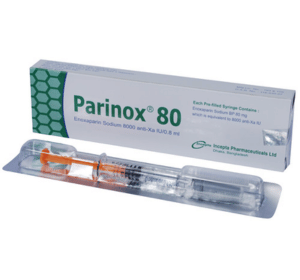
Parinox 80: Each pre-filled syringe (0.8ml) contains 8000 anti-Xa IU is equivalent to 80 mg Enoxaparin Sodium BP.
Description
Enoxaparin is a low molecular weight heparin with a high anti-Xa activity and with a low anti-lla or anti- thrombin activity. At doses required for the various indications, Enoxaparin does not increase bleeding time. At preventive doses, Enoxaparin causes no notable modification of activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT). It neither influences platelet aggregation nor binding of fibrinogen to platelets. Enoxaparin is primarily metabolized in the liver.
Indications
Enoxaparin is indicated for:
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis, with or without pulmonary embolism.
Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, administered concurrently with
aspirin.
Prevention of thrombus formation in the extra-corporal circulation during haemodialysis.
Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease (prevention of blood clot formation in the veins), in
particular those which may be associated with orthopedic or general surgery.
Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in medical patients bedridden due to acute illness,
including cardiac insufficiency, respiratory failure, severe infections, rheumatic diseases.
Dosage & Administration
Dosage adjustment in renal impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with moderate (creatinine clearance 30-50 ml/min) and mild (creatinine clearance 50-80 ml/min) renal impairment. But, all such patients should be observed carefully for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
For patients with severe (creatinine clearance <30 ml/min) renal impairment the dosage adjustment for Prophylactic dose is: 2000 IU once daily and Therapeutic dose is: 100 IU/kg once daily.
Elderly: No dosage adjustment is necessary, unless kidney function is impaired.
Children: Safety and effectiveness of Enoxaparin in pediatric patients have not been established.
Side Effects
Haemorrhage (bleeding), Thrombocytopenia, elevations of serum aminotransferase. Pain, bluish marks at injection sites to skin rash at injection sites. Cases of neuraxial hematomas with the concurrent use of Enoxaparin and spinal/epidural anesthesia or spinal puncture have resulted in varying degrees of neurologic injuries.
Precautions
Enoxaparin injection should not be administered by intramuscular route. Enoxaparin should be used with caution in conditions with increased potential for bleeding, such as impaired hemostasis, history of peptic ulcer, recent ischemic stroke, uncontrolled severe arterial hypertension, diabetic retinopathy, recent neuro or opthalmologic surgery and low weight patients. It is recommended that the platelet count be measured befored the initiation of the treatment and regularly thereafter during treatment.
Use in Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy
Pregnancy category B. In humans, there is no evidence that Enoxaparin crosses the placental barrier Enoxaparin should be used during pregnancy only if the physician has established a clear need. Enoxaparin is not recommended for use in pregnant women with prosthetic heart valves.
Lactation
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Enoxaparin injection is administered to nursing women.
Over Dose
Accidental overdosage following administration of Enoxaparin may lead to hemorrhagic complications. Injected Enoxaparin may be largely neutralized by the slow i.v. injection of protamine sulfate (1% solution) The dose of protamine sulfate should be equal to the dose of Enoxaparin injected: 1 mg protamine sulfate should be administered to neutralize 1 mg Enoxaparin.
Storage
Enoxaparin should be stored below 25° C. Do not freeze.
Commercial Pack
Parinox 20: Each box contains 1 pre-filled syringe (0.2 ml) containing 2000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to Enoxaparin Sodium BP 20 mg in a blister pack.
Parinox 40: Each box contains 1 pre-filled syringe (0.4 ml) containing 4000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to Enoxaparin Sodium BP 40 mg in a blister pack.
Parinox 60: Each box contains 1 pre-filled syringe (0.6 ml) containing 6000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to Enoxaparin Sodium BP 60 mg in a blister pack.
Parinox 80: Each box contains 1 pre-filled syringe (0.8 ml) containing 8000 anti-Xa IU equivalent to Enoxaparin Sodium BP 80 mg in a blister pack.